This
Workflow for Configuring the SyncPack
The following workflows describe how to configure the Google Cloud Platform, Skylar One, and PowerFlow to work with the "Ansible" SyncPack.
Configuring the Google Cloud Platform
See the steps in Configuring the Google Cloud Platform, below.
Configuring Skylar One
- Create a SOAP/XML credential to access PowerFlow
- Edit the Google Cloud Platform run book actions
- Enable the Google Cloud Platform run book automations
Configuring PowerFlow
- Create and align a PowerFlow configuration object
- Configure the Google Cloud Platform PowerFlow applications
- Schedule the PowerFlow applications
Configuring the Google Cloud Platform
- Create a Project in Google Cloud. Give the project a name and location, and take note of the Project ID.
- Create a Service Account and Credentials. Give the service account a name and ID, and select Owner for the Role. In the newly-created service account, go to the Keys section and create a key with type JSON.
- Configure a Google Cloud Pubsub Topic and Subscription. In the Pubsub page, create a new topic with Add a default description selected.
- Enable the Cloud Tasks API. In the Cloud Tasks page, click the button.
- Create a Cloud Tasks Push Queue. In the Cloud Tasks page, click Create Push Queue. Give the queue a name, select a region from the drop-down menu, and then click .
- Enable the Error Reporting API. In the Error Reporting page, click Set Up Error Reporting to be directed to the Guides page. In the Guides page, in the Setup Guide section click Error Reporting REST API. In the Reference page, click .
Configuring Skylar One
The following topics cover how to set up your Skylar One instance to work with the "Google Cloud Platform" SyncPack.
Creating a SOAP/XML Credential for Google Cloud Platform
You will need to create a SOAP/XML credential so that the action policies included in the "Google Cloud Platform Automations" PowerPack can access your PowerFlow system.
The "Google Cloud Platform Automations" PowerPack includes a template for a SOAP/XML credential that you can edit for use with your PowerFlow system.
To create a SOAP/XML credential:
- In Skylar One, go to the Credentials page (Manage > Credentials).
- Locate the "PowerFlow Google Cloud" sample credential, click its icon (
), and then select Duplicate. A copy of the credential, called "PowerFlow Google Cloud copy" appears.
- Supply values in the following fields:
- Name. Type a new name for the credential.
- All Organizations. Toggle on (blue) to align the credential to all organizations, or toggle off (gray) and then select one or more specific organizations from the What organization manages this service? drop-down field to align the credential with those specific organizations.
- URL. Type the URL for your PowerFlow system.
- HTTP Auth User. Type the username for your PowerFlow system.
- HTTP Auth Password. Type the password for your PowerFlow system.
- Click .
- Take note of the Skylar One-assigned ID number for the new credential on the Credentials page, in the ID column. You will need the ID number when editing the input parameters of the run book actions included in the PowerPack, below.
Editing the Google Cloud Platform Run Book Actions
The "Google Cloud Platform Automations" PowerPack includes the following run book action policies:
- "Google: Acknowledge Message"
- "Google: Delete Task"
- "Google: Event to Build"
- "Google: Event to Error"
- "Google: Event to Task"
- "Google: Publish to Pubsub"
These action policies use the "Run Integration Service Application" action type to trigger the corresponding PowerFlow application that collects data from Ansible. You can specify the credential ID in a JSON structure that you enter in the Input Parameters field in the Action Policy Editor modal.
To edit the action policies included in the PowerPack:
- In Skylar One, go to the Actions page (Registry > Run Book > Actions).
- Locate the Google Cloud Platform action policy that you want to use, and then click its wrench icon (
 ). The Editing Action page appears.
). The Editing Action page appears. - In the Input Parameters field, change the values of the following parameters:
- credential_id. Change the value to the credential ID that you noted earlier when creating a credential for your PowerFlow system in the previous procedure. This parameter is required.
- include_event. Leave the value as "true".
- application_name. Leave the default application value.
- params. Leave the default parameter value.
- Make sure the Action State is set to Enabled, and then click .
Enabling the Google Cloud Platform Run Book Automations
The "Google Cloud Platform Automations" PowerPack includes the following automation policies, which synchronize events in Skylar One and automate creating tasks, deleting tasks, starting builds, reporting errors, and publishing Pub/Sub API messages with Google Cloud Platform:
- "Google: Acknowledge Message"
- "Google: Delete Task"
- "Google: Event to Build"
- "Google: Event to Error"
- "Google: Event to Task"
- "Google: Publish to Pubsub"
When an event is detected in Skylar One, a task, build, or error is triggered in the Google Cloud Platform. When a message is detected in Skylar One, the associated message is acknowledged in the Google Cloud Platform and published to Pub/Sub.
If a policy is not already enabled, you can enable it by doing the following:
- In Skylar One, go to the Automation page (Registry > Run Book > Automation).
- Locate the automation policy you want to enable and click its wrench icon (
 ). The Automation Policy Editor page appears.
). The Automation Policy Editor page appears. - Update the following fields:
- Policy State. Select Enabled.
- Policy Priority. Select Default to ensure that this PowerFlow automation policy is added to the top of the queue.
- Available Actions. If it is not already selected, select the Google automation action that corresponds with the automation policy you selected in step 2, and click the arrows to move it to Aligned Actions.
By default, the "GCP: Publish to Pubsub" automation policy will create Google Cloud Platform events for all devices. You can limit the devices affected by making changes to the Organization, Severity, Match Logic, Aligned Devices, and/or Aligned Events fields.
ScienceLogic highly recommends that you do not make changes to the Policy Type, Repeat Time, or Align With fields or the And event is NOT acknowledged setting.
- Click .
- Repeat steps for any other run book automation policies that need to be enabled.
Configuring PowerFlow
Creating and Aligning a Configuration Object in PowerFlow
A configuration object supplies the login credentials and other required information needed to execute the steps for a PowerFlow application. The Configurations page () of the PowerFlow user interface lists all available configuration objects for that system.
You can create as many configuration objects as you need. A PowerFlow application can only use one configuration object at a time, but you can use (or "align") the same configuration object with multiple applications.
To use this SyncPack, you will need to use an existing configuration object in the PowerFlow user interface or create a new configuration object. Next, you need to align that configuration object to the relevant applications.
Creating a Configuration Object
For this SyncPack, you can make a copy of the "GCP Base Config" configuration object, which is the sample configuration file that was installed with the "Google Cloud Platform" SyncPack.
The "GCP Base Config" configuration object contains all of the required variables. Simply update the variables from that object to match your Skylar One and Google Cloud Platform settings.
To create a configuration object based on the "GCP Base Config" configuration object:
- In the PowerFlow user interface, go to the Configurations page (
).
-
Click the button (
) for the "GCP Base Config" configuration object and select Edit. The Configuration pane appears.
- Click . The Create Configuration pane appears.
- Complete the following fields:
- Friendly Name. Type a name for the configuration object that will display on the Configurations page.
- Description. Type a brief description of the configuration object.
- Author. Type the user or organization that created the configuration object.
- Version. Type a version of the configuration object.
- In the Configuration Data field, update the default variable definitions to match your PowerFlow configuration:
- sl1_host. Type the hostname or IP address of your Skylar One system.
- sl1_user. Type the username for your Skylar One system.
- sl1_password. Type the password for your Skylar One system.
- populate_external_url. Type 'enabled' or 'disabled' to add a Google Cloud Platform URL to the corresponding Skylar One event. The default value is 'enabled'.
- gcp_project_id. The unique ID associated with a Google Cloud Platform project. This value is filled in using the "project_id" parameter in the JSON credentials file.
- gcp_private_key_id. The unique key ID required for authenticating with Google Cloud. This value is filled in using the "private_key_id" parameter in the JSON credentials file.
- gcp_private_key. The unique key required for authenticating with Google Cloud. This value is filled in using the "private_key" parameter in the JSON credentials file.
- gcp_client_email. The generated email associated with the client in the Google Cloud Platform. This value is filled in using the "client_email" parameter in the JSON credentials file.
- gcp_client_id. The ID associated with the client in the Google Cloud Platform. This value is filled in using the "client_id" parameter in the JSON credential file.
- gcp_client_x509_cert_url. The client certificate URL associated with the client in the Google Cloud Platform. This value is filled in using the "client_x509_cert_url" parameter in the JSON credential file.
- gcp_pubsub_subscriber_audience. Type subscriber client URL for your Pub/Sub account.
- gcp_pubsub_publisher_audience. Type publisher client URL for your Pub/Sub account.
- gcp_pubsub_topic_id. Type the topic ID for Pub/Sub messages.
- gcp_pubsub_subscription_id. Type the subscription ID for your Pub/Sub account.
- gcp_pubsub_timeout. Type the number of seconds between retrying to communicate with Pub/Sub.
- gcp_pubsub_deadline. Type the number of seconds to retry Pub/Sub after execution. After the defined number of seconds, the SyncPack will stop attempting to communicate with Pub/Sub.
- gcp_pubsub_num_messages. Type the number of messages to pull from Pub/Sub.
- gcp_task_queue. Type the name of the queue for the Google Cloud Platform tasks.
- gcp_task_location. Type the default location for the Google Cloud Platform task.
- gcp_task_url. Type the URL for your Cloud Tasks account.
- gcp_task_seconds_from_now. Type the scheduled time in seconds to create a task in Google Cloud Platform.
- gcp_build_steps. Type the Google Cloud Platform build steps to execute when the build is successful in Cloud Build.
- add_template. Toggle the JSON editor to define the template to translate Skylar One event information to a Google Cloud Platform task, error, or message.
- Click . You can now align this configuration object with one or more applications.
Aligning a Configuration Object and Configuring PowerFlow Applications
With this SyncPack, any status changes made to a Skylar One event is sent to the Google Cloud Platform to update the corresponding task, error, or message. Any status changes to the Google Cloud Platform task or error are synchronized back to the corresponding Skylar One event.
You will need to align the Google Cloud Platform applications with the relevant configuration object in PowerFlow, and, if needed, update any other fields on the Configuration pane for the applications.
To align the configuration object with the relevant PowerFlow applications:
-
On the Applications page of the PowerFlow user interface, open one of the PowerFlow applications listed above and click (
). The Configurations pane for that application appears.
-
From the Configurations drop-down, select the configuration object you want to use.
The values for sl1_hostname and the other parameters that appear in the Configuration pane with a padlock icon (
) are populated by the configuration object you aligned with the application. Do not modify these values. If you encounter an error, make sure your configuration object is configured properly.
-
Update the remaining fields on the Configurations pane as needed, and then click .
-
Repeat this process for the other PowerFlow applications.
Scheduling PowerFlow Applications
To trigger the PowerFlow applications in the SyncPack, you must schedule the applications.
You can create one or more schedules for a single application in the PowerFlow user interface. When creating each schedule, you can specify the queue and the configuration file for that application.
To create a schedule:
- On the Applications page (
), click the button for the application you want to schedule. The Scheduler window appears.
- In the Schedule List pane, click the down arrow icon (
) next to an existing schedule to view the details for that schedule.
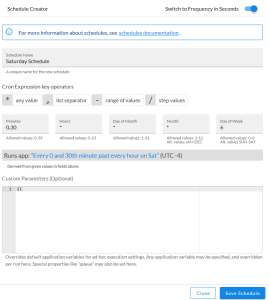
- In the Schedule Creator pane, complete the following fields for the default Frequency setting:
- Schedule Name. Type a name for the schedule.
- Frequency in seconds. Type the number of seconds per interval that you want to run the application.
- Custom Parameters. Type any JSON parameters you want to use for this schedule, such as information about a configuration file or mappings.
- To use a cron expression, click the Switch to Cron Expression toggle to turn it blue. If you select this option, you can create complicated schedules based on minutes, hours, the day of the month, the month, and the day of the week:
As you update the cron expression, the Schedule window displays the results of the expression in more readable language, such as Runs app: "Every 0 and 30th minute past every hour on Sat", based on 0,30 in the Minutes field and 6 in the Day of Week field.
- Click . The schedule is added to the Schedule List pane. Also, on the Applications page, the button now displays with a dark blue background:
After you create a schedule, it continues to run until you delete it. Also, you cannot edit an existing schedule, but you can delete it and create a similar schedule if needed.
To view or delete an existing schedule:
- On the Applications page, click the button for the application that contains a schedule you want to delete. The Scheduler window appears.
- Click the down arrow icon (
) to view the details of an existing schedule.
- To delete the selected schedule, click the Actions icon (
) and select.
On the Scheduler window for a PowerFlow application, you can click the button from the Schedule List pane to make a copy of an existing schedule.
When either multiple Skylar One instances or multiple Google Cloud Platform instances are involved with PowerFlow, you should create an individual configuration object for each Skylar One or Google Cloud Platform instance. Next, create an individual schedule for each configuration object. Each schedule should use a configuration object that is specific to that single Skylar One or Google Cloud instance. Creating copies of a PowerFlow application from a SyncPack for the purpose of distinguishing between domains is not supported, and will result in issues on upgrades.