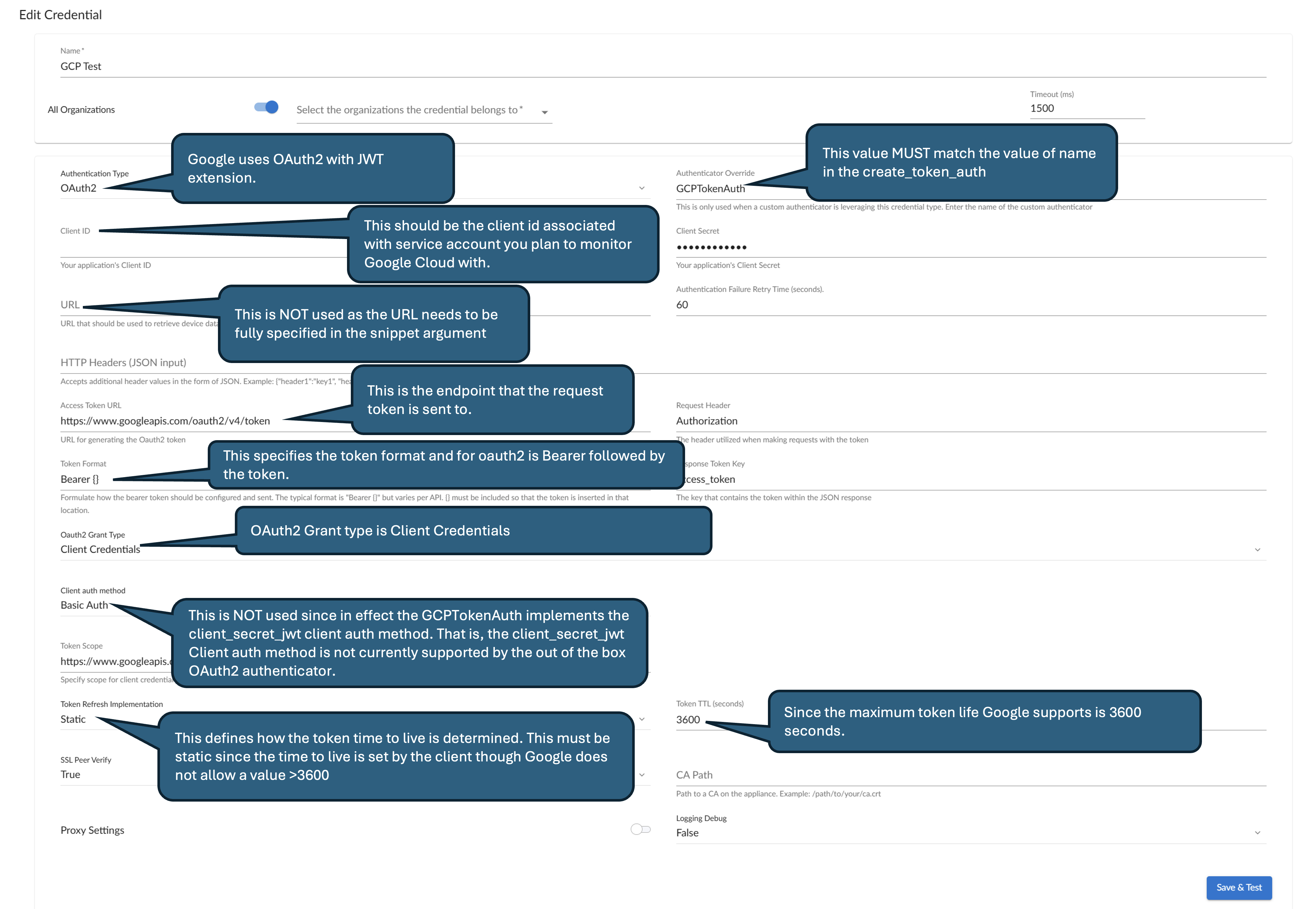
Google Cloud OAuth2 Example
The following example shows how the OAuth2 Authenticator can be extended to
support JWT. This example demonstrates authenticating to the Google Cloud API.
The OAuth2 Authenticator supports a token request with a payload that includes
grant_type, client_id, client_secret and scope. These fields are
retrieved from the credential. When using JWT the payload to be sent is as
follows:
{
"data": {
"grant_type": "urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer",
"assertion": "signature"
}
}
Since the only thing that is different between the out of the box OAuth2
Authenticator and the JWT extension is the payload sent in the initial token
request, the only hook required in this case is the get_token_request_args.
It will be setting the payload as above. The code for the GCP Authenticator is
shown below. The first step is to build the payload using the fields taken from
the credential. The next step is to calculate the signature. The last step is to
return the payload as specified.
import time,jwt
from silo.auth import create_oauth_authenticator
def get_token_request_data(credential,logger):
payload = {
"iss": credential.fields["oauth2ClientId"],
"scope": credential.fields["oauth2ClientCredentialsScope"],
"aud": credential.fields["oauth2TokenURL"],
"exp": int(time.time()) + credential.fields["tokenRefreshTTL"],
"iat": int(time.time()),
}
signature = jwt.encode(
payload,
credential.fields["oauth2ClientSecret"].replace("\\n", "\n"),
algorithm="RS256",
headers={"alg": "RS256", "typ": "JWT"},
)
return {
"data": {
"grant_type": "urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer",
"assertion": signature,
},
}
create_oauth_authenticator(
name="GCPTokenAuth",
description="Token Authentication for GCP",
get_token_request_args=get_token_request_data,
)
Snippet Argument
low_code:
version: 2
steps:
- http:
url: >-
https://serviceusage.googleapis.com/v1/projects/rebelscrum-new/services?filter=state:ENABLED
- json
- jmespath:
value: services[*].config.name
Google GCP Credential