This
For more information about creating automation policies using custom action types, see Creating and Customizing Automation Policies.
Creating a Custom Action Policy
You can use the "Restorepoint: Generic Action type" action type included with the "Restorepoint Automation" PowerPack to create custom automation actions that you can then use to build custom automation policies.
To create a custom action policy using the "Restorepoint: Generic Action type" action type:
- Navigate to the Action Policy Manager page (Registry > Run Book > Actions).
- In the Action Policy Manager page, click the button.
- The Action Policy Editor modal appears.
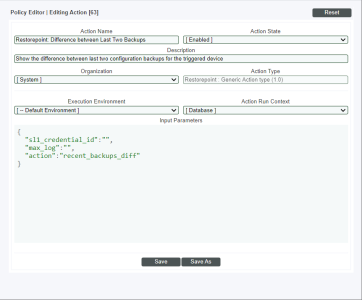
- In the Action Policy Editor page, supply a value in each field:
- Action Name. Specify the name for the action policy.
- Action State. Specifies whether the policy can be executed by an automation policy (enabled) or cannot be executed (disabled).
- Description. Allows you to enter a detailed description of the action.
- Organization. Organization to associate with the action policy.
- Action Type. Type of action that will be executed. Select the "Restorepoint: Generic Action type" action type (highlighted in the figure above).
- Execution Environment. Select from the list of available Execution Environments. The default execution environment is System.
- Action Run Context. Select Database or Collector as the context in which the action policy will run.
- Input Parameters. A JSON structure that specifies each input parameter. Each parameter definition includes its name, data type, and whether the input is optional or required for this Custom Action Type.Input parameters must be defined as a JSON structure, even if only one parameter is defined.
-
Click [Save]. If you are modifying an existing action policy, click . Supply a new value in the Action Name field, and save the current action policy, including any edits, as a new policy.
Customizing Automation Actions
The "Restorepoint Automation" PowerPack includes 3 automation actions that use the "Restorepoint: Generic Action type" action type to request diagnostic information or remediate an issue. You can specify the host and the options in a JSON structure that you enter in the Input Parameters field in the Action Policy Editor modal.
The run book automations only work against devices that have the Restorepoint ID custom attribute, which is automatically set when a device is synchronized from Skylar One to Restorepoint. The automation actions share formatting actions with the Datacenter Automation Pack, so the output can be sent to Restorepoint using the same customization steps.
The following automation actions that use the "Restorepoint: Generic Action type" action type are included in the PowerPack. Compare the commands run with the example in the image above.
| Action Name | Description | Commands Run |
|---|---|---|
|
RestorepointRecent Logs |
Collects the last number of logs for the device associated with the triggering event. The number of logs is configurable. |
|
|
Link to Configuration Backup |
Creates a link to the Restorepoint UI that displays the last configuration backup from the device associated with the triggering event. |
|
|
Difference between Last Two Backups |
Collects the difference between the last two configuration backups for the device associated with the triggering event. |
|
For more information about substitution variables, see Appendix A: Run Book Variables.
Creating a New Restorepoint Automation Action
You can create a new automation action or you can also use the existing automation actions in the PowerPack as a template by using the [Save As] option.
The automation actions accept the following parameters in JSON:
| Parameter | Input type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
sl1_credential_id |
integer |
The ID of the credential to use when running the command. The credential connects to the Restorepoint API to gather data. |
|
max_log |
integer |
The number of log entries to collect from Restorepoint. |
|
action |
string
|
The data to collect from Restorepoint. There are three support values for this parameter:
|
Using Substitution Values. The command input can contain substitution values that match the keys in EM7_VALUES.
For more information about substitution variables, see Appendix A: Run Book Variables.
For a description of all options that are available in Automation Policies, see the