The following sections describe how to configure a Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CM) system for monitoring by Skylar One using the "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack.
Prerequisites for Monitoring CUCM
During the discovery process, Skylar One automatically aligns the IP addresses and hostnames for each node in a Cisco Unified CM cluster via DNS.
If you do not have access to DNS for the Cisco Unified CM systems that you want to monitor with Skylar One, ensure that you know or have access to the following information about each node:
- IP address
- Hostname
Configuring Skylar One to Monitor CUCM
You can choose from several different possible configurations when using Skylar One to monitor Cisco Unified CM:
- You can have the ScienceLogic Data Collector either in front of a firewall or behind a firewall.
- You can define the CallManager nodes either by hostname or by IP address in the Cisco Unified CM database.
- In some scenarios, you can also use network address translation (NAT) when defining the CallManagers.
These various methods are described in this section.
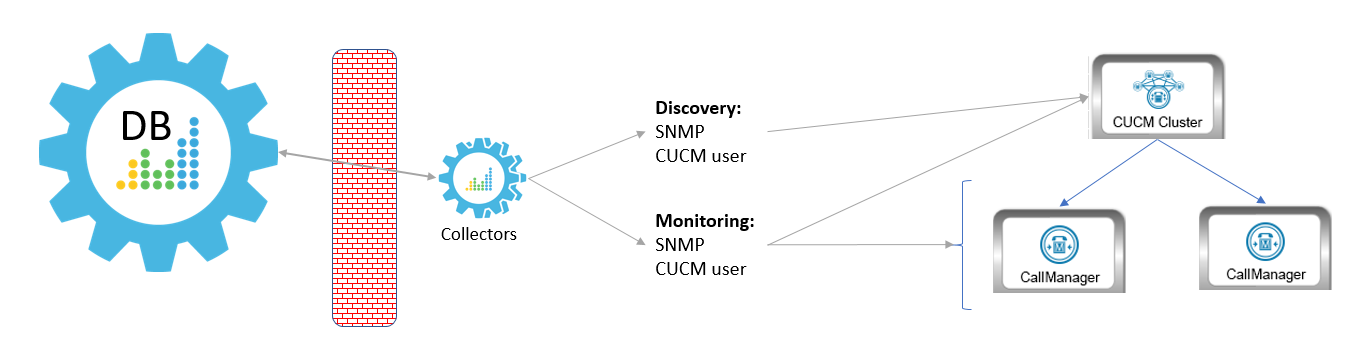
Method 1
In the first scenario, the Data Collector sits in front of the firewall and you define the CallManagers by hostname:
In this scenario, you must have the following ports open for the firewall:
| Direction | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| ScienceLogic Database Server to the Data Collector | 7707 | TCP |
| PhoneHome Collector to the Database Server | 7705 | TCP |
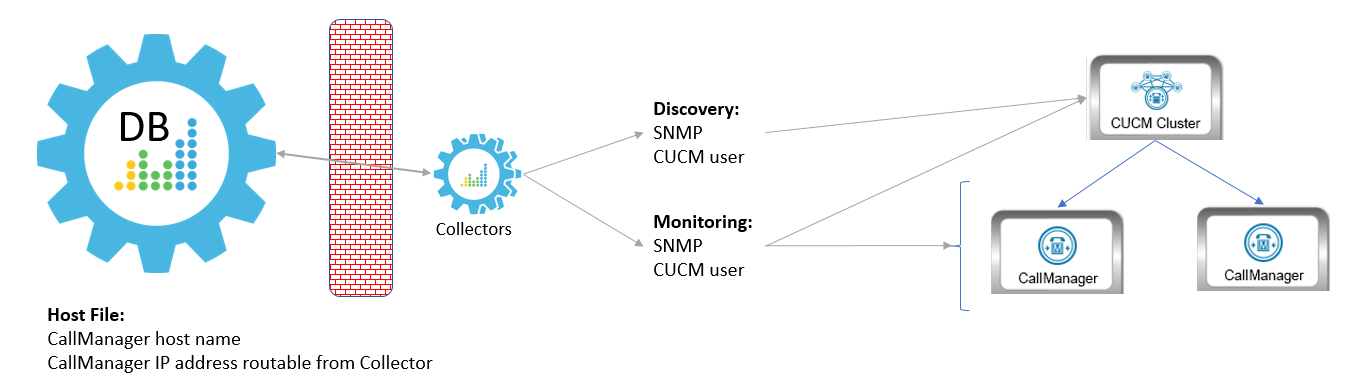
Method 2
In the second scenario, the Data Collector sits in front of the firewall and you define the CallManagers by IP address. This method requires you to create a host file that includes the CallManager hostname and IP address:
In this scenario, you must have the following ports open for the firewall:
| Direction | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| ScienceLogic Database Server to the Data Collector | 7707 | TCP |
| PhoneHome Collector to the Database Server | 7705 | TCP |
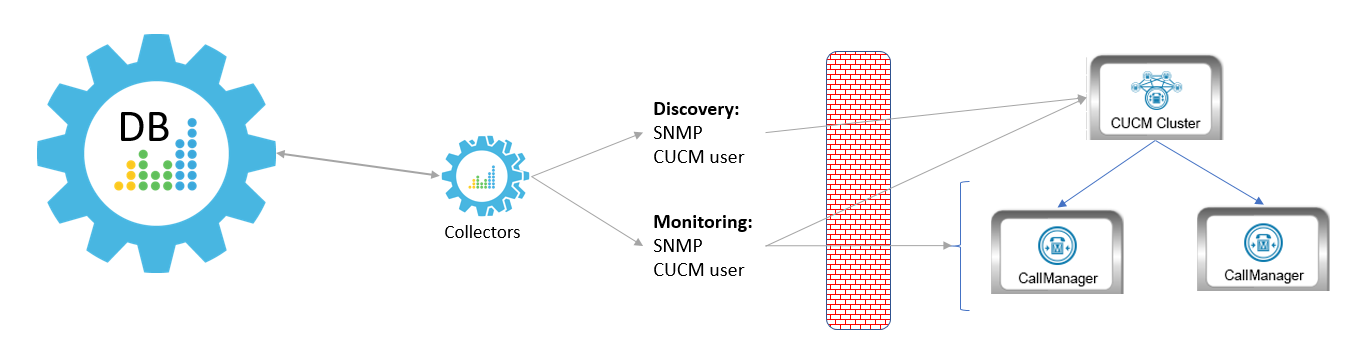
Method 3
In the third scenario, the Data Collector sits behind the firewall and you define the CallManagers by hostname:
In this scenario, you must have the following ports open for the firewall:
| Direction | Credential | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ScienceLogic Data Collector to the Cisco Unified CM Cluster and CallManagers | SNMP | 161 | UDP |
| Cisco Unified CM user | 8443 | TCP |
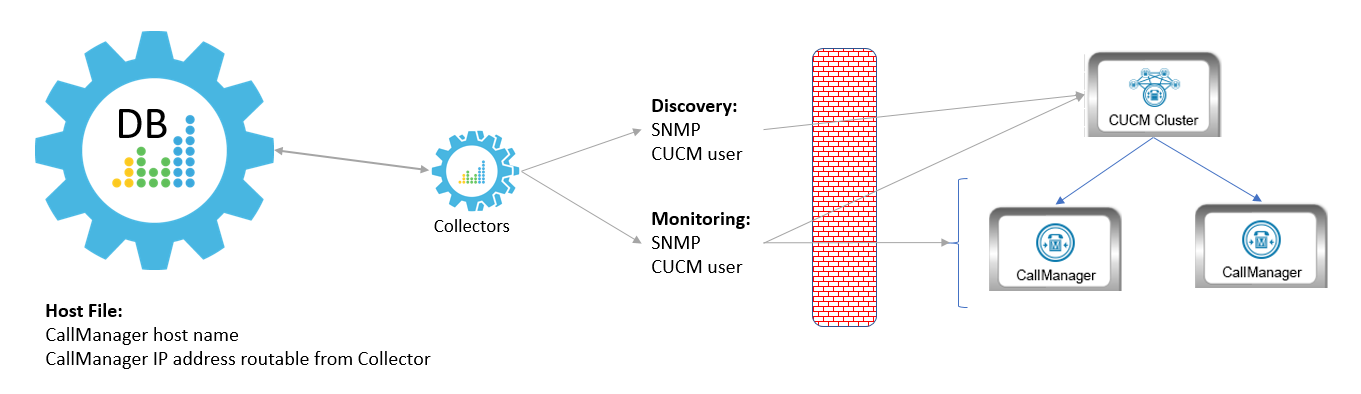
Method 4
In the fourth scenario, the Data Collector sits behind the firewall and you define the CallManagers by hostname, with NAT. This method requires you to create a host file that includes the CallManager hostname and the IP address the Data Collector can use to access the device:
In this scenario, you must have the following ports open for the firewall:
| Direction | Credential | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ScienceLogic Data Collector to the Cisco Unified CM Cluster and CallManagers | SNMP | 161 | UDP |
| Cisco Unified CM user | 8443 | TCP |
Method 5
In the final scenario, the Data Collector sits behind the firewall and you define the CallManagers by IP address, with NAT. This method requires you to create a host file that includes the CallManager host name and IP address the Data Collector can use to access the device:
This method is not supported by versions of the "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack prior to version 109.
In this scenario, you must have the following ports open for the firewall:
| Direction | Credential | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ScienceLogic Data Collector to the Cisco Unified CM Cluster and CallManagers | SNMP | 161 | UDP |
| Cisco Unified CM user | 8443 | TCP |
Configuring CUCM for NAT
If you are using Network Address Translation (NAT) in your environment, you will need to adjust a threshold in the "Cisco: CUCM Cluster Information" Dynamic Application to enable NAT support.
To configure the threshold object:
- Go to the Dynamic Applications Manager page (System > Manage > Dynamic Applications).
- Locate the "Cisco: CUCM Cluster Information" Dynamic Application and click its wrench icon (
 ).
). - In the Dynamic Applications Properties Editor, click the tab.
- Click the wrench icon (
 ) for the "Use Server Hostname for NAT" threshold object.
) for the "Use Server Hostname for NAT" threshold object. - Ensure that the Override Threshold Value field is set to Enabled.
- In the Threshold Value field, type "1".
NOTE: The Threshold Value will be reset when you upgrade the PowerPack if you have not enabled the Enable Selective PowerPack Field Protection setting. To do this, go to the Behavior Settings page (System > Settings > Behavior) and click the Enable Selective PowerPack Field Protection checkbox.
- Click .
Enabling the CUCM AXL Web Service
Skylar One can monitor a Cisco Unified CM system by requesting detailed information about the system from the Cisco Unified CM AXL Web Service.
The Cisco Unified CM AXL web service is disabled by default. To enable the AXL web service, perform the following steps:
- In a browser window, navigate to the following address:
- Log in to the Cisco Unified CM Administration site as an administrator.
- In the Navigation drop-down list at the top-right corner of the page, select Cisco Unified Serviceability, and then click the button. The Cisco Unified Serviceability page appears.
- In the navigation bar at the top-left of the page, hover over Tools, then select Service Activation. The Service Activation page appears.
- In the Server drop-down list, select the Cisco Unified CM server for which you want to enable the AXL web service, and then click the button.
- In the list of services, locate the Database and Admin Services section. If the Activation Status of the Cisco AXL Web Service is "Activated", the AXL web service is already enabled.
- If the Activation Status of the Cisco AXL Web Service is not "Activated", select the checkbox for the Cisco AXL Web Service.
- Click the button at the bottom of the page to save your changes, and then click the button in the pop-up window that appears.
https://ip-address-of-CM-system:8443/ccmadmin/showHome.do
Configuring a CUCM User Account
ScienceLogic recommends that you create a Cisco Unified CM user account that will be used only by Skylar One to access the AXL web service. To create a user account in Cisco Unified CM that can access only the AXL web service, perform these two steps:
- Create a user account.
- Create a user group that includes the user account and has permission to access only the AXL web service.
To create a new Cisco Unified CM user group and user account, perform the following steps:
- In a browser window, navigate to the following address:
https://ip-address-of-CM-system:8443/ccmadmin/showHome.do
- Log in to the Cisco Unified CM Administration site as an administrator.
- In the navigation bar at the top-left of the page, hover over User Management, then select Application User. The Find and List Users page appears.
- Click the button. The Application User Configuration page appears.
- Supply values in the following fields:
- User ID. Type a username for the new user.
- Password. Type a password for the new user.
- Confirm Password. Type the password for the new user again.
- Click the button.
- In the navigation bar at the top-left of the page, hover over User Management, then select User Group. The Find and List User Groups page appears.
- Click the button. The User Group Configuration page appears.
- In the Name field, type a name for the user group. For example, you could call the user group "AXL Access".
- Click the button.
- Click the button. The Find and List Application Users window appears.
- Click the button. In the list of users, select the checkbox for the user account that you created, then click the button at the bottom of the page.
- The Find and List Application Users window closes. In the User Group Configuration page, the user account is included in the list of users
- In the Related Links drop-down list at the top-right hand corner of the page, select Assign Role to User Group, and then click the button. The User Group Configuration page appears.
- Click the button. The Find and List Roles window appears.
- Click the button. A list of roles appears.
- Select the checkboxes for the following roles:
- Standard AXL API Access
- Standard CCM Admin Users
- Standard SERVICEABILITY Read Only
- Click the button at the bottom of the page.
- The Find and List Roles window closes. In the User Group Configuration page, the Roles field includes the Standard AXL API Access role.
- Click the button.
Configuring Prime License Manager
If you want to monitor Cisco Unified CM license information from Cisco Prime License Manager (PLM), you must create an administrator user account that Skylar One can use to access PLM.
To create an administrator user in PLM:
- In a browser window, navigate to the following address:
https://ip-address-of-plm-server/elm-admin/
- Log in to the Cisco PLM site as an administrator.
- In the Administration drop-down menu, select Administrator Accounts.
- Click the button.
- In the Add Administrator Account modal page, make entries in the following fields.
- Name/Description. Type a name or description for the account.
- Username. Type the account username.
- Password. Type the account password.
- Re-enter Password. Type the account password again.
- Click .
Creating a CUCM Credential
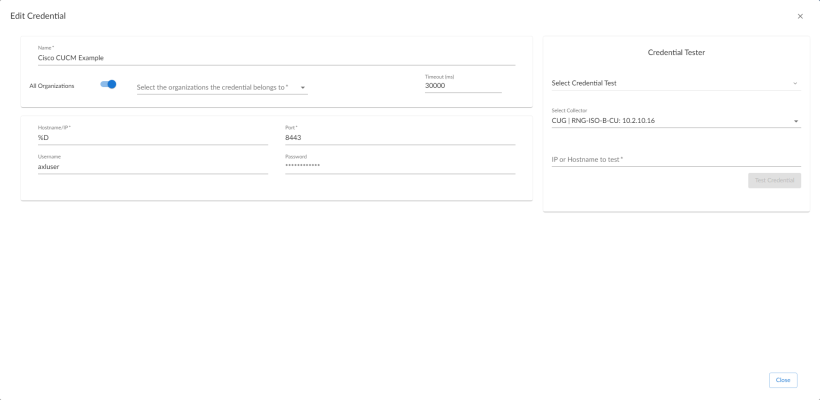
To use the Dynamic Applications in the "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack, you must first define a Basic/Snippet Cisco Unified CM credential in Skylar One. This credential allows Skylar One to communicate with the Cisco Unified CM cluster. The "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack includes a template you can use to create this Basic/Snippet credential.
NOTE: If you are using a Skylar One system prior to version 11.1.0, the new user interface does not include the Duplicate option for sample credential(s). ScienceLogic recommends that you use the classic user interface and the Save As button to create new credentials from sample credentials. This will prevent you from overwriting the sample credential(s).
To modify the Cisco Unified CM Basic/Snippet Credential template for use with your Cisco Unified CM cluster:
- Go to the Credentials page (Manage > Credentials).
-
Locate the "Cisco CUCM Example" sample credential. Click its icon (
) and select Duplicate. A copy of the credential, called Cisco CUCM Example copy appears.
- Click the icon (
) for the Cisco CUCM Example copy credential and select Edit. The Edit Credential page appears:
- Supply values in the following fields:
-
Name. Type a new name for the credential.
-
All Organizations. Toggle on (blue) to align the credential to all organizations, or toggle off (gray) and then select one or more specific organizations from the What organization manages this service? drop-down field to align the credential with those specific organizations.
-
Timeout (ms). Type the timeout value of each request, in milliseconds. The default value is "30000".
- Hostname/IP. Type the hostname or IP address, or you can type the variable "%D".
- Port. Type the port number.
The example credential included in older versions of the "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack used "80" as the default Port number. If your Cisco Unified CM credential specifies port 80, Skylar One will automatically override that value and use port 8443 instead. If your Cisco Unified CM credential specifies any port other than 80, Skylar One will use that specified port.
- Username. Type the username for the Cisco Unified CM user account that you created to access the AXL web service. For details, see the Configuring a Cisco Unified CM User Account section.
- Password. Type the password for the username you entered in the Username field.
- Click .
Creating a CUCM Credential in the Skylar One Classic User Interface
To use the Dynamic Applications in the "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack, you must first define a Basic/Snippet Cisco Unified CM credential in Skylar One. This credential allows Skylar One to communicate with the Cisco Unified CM cluster. The "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack includes a template you can use to create this Basic/Snippet credential.
To modify the Cisco Unified CM Basic/Snippet Credential template for use with your Cisco Unified CM cluster:
- Go to the Credential Management page (System > Manage > Credentials).
- Click the wrench icon (
 ) for the Cisco CUCM Example credential. The Credential Editor modal window appears.
) for the Cisco CUCM Example credential. The Credential Editor modal window appears. - Supply values in the following fields:
- Credential Name. Type a new name for the credential.
- Hostname/IP. Type the hostname or IP address, or you can type the variable "%D".
- Port. Type the port number.
The example credential included in older versions of the "Cisco: CUCM Unified Communications Manager" PowerPack used "80" as the default Port number. If your Cisco Unified CM credential specifies port 80, Skylar One will automatically override that value and use port 8443 instead. If your Cisco Unified CM credential specifies any port other than 80, Skylar One will use that specified port.
- Timeout (ms). Type the timeout value of each request, in milliseconds. The default value is "30000".
- Username. Type the username for the Cisco Unified CM user account that you created to access the AXL web service. For details, see the Configuring a Cisco Unified CM User Account section.
- Password. Type the password for the username you entered in the Username field.
- Click the button.
If you are monitoring Cisco Unified CM license information with the Cisco Prime License Manager (PLM) and your PLM administrator username and password are the same as the user account you created to access the AXL web service, then you can use the same credential to access PLM. However, if your PLM administrator user information is different, then repeat these steps to create a credential to access PLM.
If SNMP is enabled on the Cisco Unified CM cluster, then you can also create an optional SNMP credential that will be used only during discovery to classify the cluster device class. If SNMP is not available on the Cisco Unified CM cluster, then you do not need an SNMP credential. For more information on SNMP credentials, see
Manually Creating Host File Entries for CUCM Nodes
During the discovery process, Skylar One automatically aligns the IP addresses and hostnames for each CallManager server (node) in a Cisco Unified CM cluster via DNS.
If you do not have access to DNS for the Cisco Unified CM system you want to monitor, you must manually create host file entries in Skylar One for each node in the Cisco Unified CM cluster. Each host file entry must contain the IP address and hostname of a node in the Cisco Unified CM cluster.
If you have access to DNS for the Cisco Unified CM system you want to monitor with Skylar One, you do not need to perform the steps to manually configure host file entries. Continue to the section on Discovering a Cisco Unified CM Cluster.
Repeat the following steps for each node in the Cisco Unified CM cluster.
To create a host file entry:
- Go to the Host File Entry Manager page (System > Customize > Host Files).
- Click the menu and choose Create New Entry. The Create New Host File Entry modal page appears.
- In the Create New Host File Entry modal page, supply values in the following fields:
- IP Address. The IP address to resolve with the hostname.
Server hostnames should be aligned to external IP addresses when supporting Network Address Translation (NAT) environments.
- Hostnames and Aliases. The hostname to align with the specified IP address. You can also include a space-delimited list of aliases for the host name.
- Description. Description of the host entry. This field is not written to the host file. This field is for administrators to use when managing host file entries.
- Organization. Organization associated with the host. You can select from a list of all existing organizations. This field is not written to the host file. This field is for administrators to use when managing host file entries. For example, a service provider could assign each customer its own organization and then use this field to manage host file entries for each customer.
- Click the button to save the new host entry.