This
What is the Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack?
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack includes:
- A set of automation actions that run diagnostic commands on Hyper-V systems via PowerShell
- A set of automation policies that tie events from monitoring PowerPacks to the automation actions
- A dynamic device group for Hyper-V devices that is used to scope the automation policies
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations actions are executed on the SL1 All-In-One Appliance or Data Collector.
In addition to using the standard content, you can use the content in the Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack to create your own automation policies that include the pre-defined actions that run different sets of diagnostic commands.
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack uses the supplied “Execute PowerShell Request” custom action type included with the Windows PowerShell Automations PowerPack.
Prerequisites
Before installing the Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack, you must perform the following actions:
- Install the Microsoft: Hyper-V Server PowerPack and configure it to monitor your Hyper-V device(s)
- Install version 103 or later of the Windows PowerShell Automations PowerPack
- Install version 102 or later of the Datacenter Automation Utilities PowerPack
- Install the Diag-V plug-in on your Hyper-V server. The plug-in is available here: https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/Diag-V-A-Hyper-V-0fe983e4
Installing the Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack
Before completing the steps in this
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack requires SL1 version 8.10.0 or later. For details on upgrading SL1, see the appropriate SL1Release Notes.
By default, installing a new version of a PowerPack overwrites all content from a previous version of that PowerPack that has already been installed on the target system. You can use the Enable Selective PowerPack Field Protection setting in the Behavior Settings page (System > Settings > Behavior) to prevent new PowerPacks from overwriting local changes for some commonly customized fields. For more information, see the section on Global Settings.
To download and install the PowerPack:
- Search for and download the PowerPack from the PowerPacks page (Product Downloads > PowerPacks & SyncPacks) at the ScienceLogic Support Site.
- In SL1, go to the PowerPacks page (System > Manage > PowerPacks).
- Click the button and choose Import PowerPack. The Import PowerPack dialog box appears.
- Click [Browse] and navigate to the PowerPack file from step 1.
- Select the PowerPack file and click . The PowerPack Installer modal displays a list of the PowerPack contents.
- Click . The PowerPack is added to the PowerPacks page.
If you exit the PowerPack Installer modal without installing the imported PowerPack, the imported PowerPack will not appear in the PowerPacks page. However, the imported PowerPack will appear in the Imported PowerPacks modal. This page appears when you click the menu and select Install PowerPack.
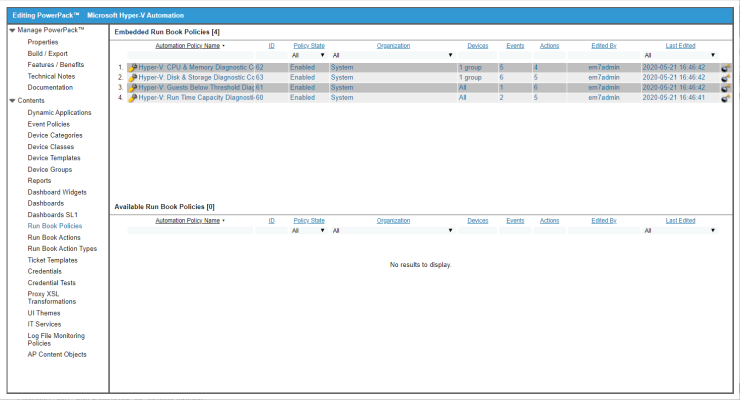
Standard Automation Policies
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack includes four standard automation policies, shown in the following figure. Each policy triggers three automation actions that collect diagnostic data within a PowerShell session, and an action that formats the output in HTML. All of the automation actions use the same custom action type, "Execute PowerShell Request", which is supplied in the Windows PowerShell AutomationsPowerPack.
All of the standard automation policies are tied to included ScienceLogic SL1 events generated by the Dynamic Applications from the Microsoft: Hyper-V Server PowerPack.
Several of the automation actions use the substitution character feature of the “Execute PowerShell Request” custom action type. If an event variable is included in a command (such as "%Y" for the sub-entity name), the custom action type automatically replaces that variable with the value from the triggering event.
The following table shows the standard automation policies, their aligned events, and the automation actions that run in response to the events.
The aligned events are included as part of the Microsoft: Hyper-V Server PowerPack and are not installed with the SL1 platform. You must install the Microsoft: Hyper-V Server PowerPack to obtain these events.
| Automation Policy Name | Aligned Events | Automation Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Hyper-V: CPU & Memory Diagnostic Commands |
|
|
| Hyper-V: Disk & Storage Diagnostic Commands |
|
|
| Hyper-V: Guests Below Threshold Diagnostic Commands |
|
|
| Hyper-V: Run Time Capacity Diagnostic Commands |
|
|
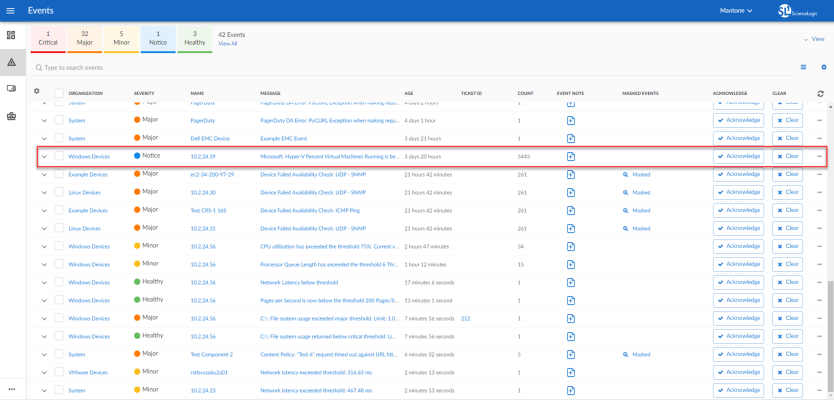
The following figure shows a memory event with a classification of "Major" appears on the Events page. Click the [Actions] button () for an event, and select View Automation Actions to see the automation actions triggered by the events.
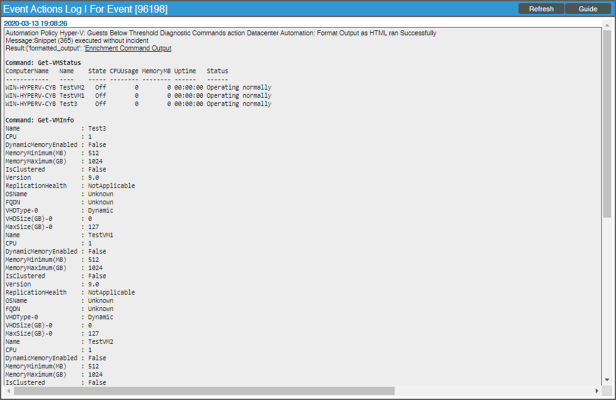
The results shown for this event, in the Event Actions Log, include the automation policy that ran (shown at the top of the following figure), along with the automation actions (commands) that ran. Results for each command are also displayed. The following figure shows an example of this HTML output.
To learn more about which commands are executed by default for a given automation action, see Customizing Actions.
Although you can edit the automation policies described in this section, it is a best practice to use "Save As" to create a new automation action, rather than to customize the standard automation policies.
Credential for Hyper-V Automation
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack uses the same credential that you created for the Windows PowerShell Automations PowerPack. Refer to the Creating a Credential section for more information.
If you have the Microsoft: Windows Server PowerPack installed and configured, you may skip this section.
For more information about configuring credentials in SL1, see Credentials.
Creating and Customizing Hyper-V Automation Policies
To create and customize Automation Policies for the Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack, see the Creating and Customizing Automation Policies section.
Creating a Custom Action Policy for Hyper-V
You can use the "Execute PowerShell Request" action type included with the Windows PowerShell Automations PowerPack to create custom automation actions that you can then use to build custom automation policies. To create a custom action policy, see the Creating a Custom Action Policy section.
Customizing Automation Actions
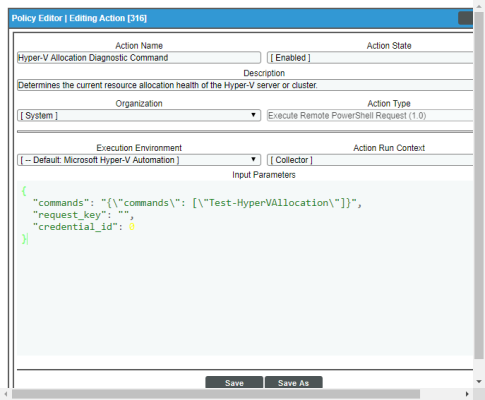
The Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack includes 2 automation actions that execute the "Execute PowerShell Request" action type to request diagnostic information or remediate an issue. You can specify the commands and the options in a JSON structure that you enter in the Input Parameters field in the Action Policy Editor modal.
The following automation actions that use the "Execute PowerShell Request" action type are included in the Microsoft Hyper-V Automations PowerPack. Compare the commands run with the example in the image above. For more information about input parameter fields,
see the table in Creating a New Microsoft Hyper-V Automation Action.
| Action Name | Description | Commands Run |
|---|---|---|
|
Hyper-V Allocation Diagnostic Command |
Determines the current resource allocation health of the Hyper-V server or cluster. |
|
| Hyper-V Guest Replication Diagnostic Command | Runs a diagnostic command related to Hyper-V guest replication |
|
|
Hyper-V Guest Status Diagnostic Commands |
Runs diagnostic commands to collect Hyper-V guest status and configuration information. |
|
| Hyper-V Guest Storage Diagnostic Commands | Runs diagnostic commands related to Hyper-V Guest storage and replication. |
|
| Hyper-V Log Collection | Collects the most recent 25 log entries from the Hyper-V logs. |
|
For more information about substitution variables, see Appendix A.
Creating a New Microsoft Hyper-V Automation Action
You can create a new automation action that runs remote PowerShell requests using the supplied "Execute PowerShell Request" custom action type. To do this, refer to the Creating a New Windows PowerShell Automation Action section
For a description of all options that are available in Automation Policies, see the